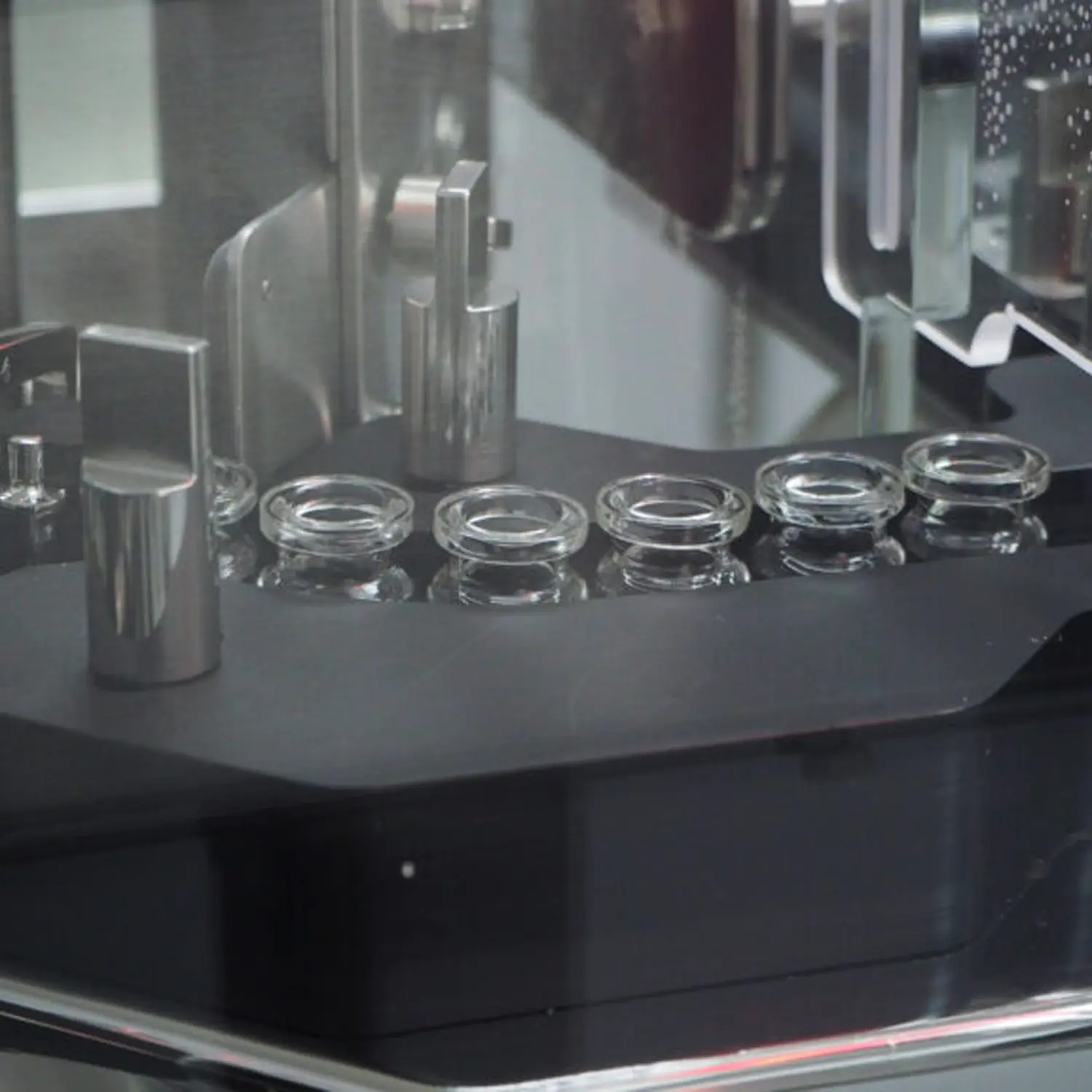

Cleaning with Water for Injection
Regulatory requirements to use WFI to clean.
The European Medicines Agency have provided guidelines on the cleaning water quality for items that come in contact with products for pharmaceutical use. Manufacturers should perform a final rinse of equipment, containers and closures with water that is the same quality of that used in the manufacture of said medical product (1).
This requirement is matched by the FDA. Water for injection (WFI) is the highest quality of water for pharmaceutical use. It is required for diluting or dissolving substances in the manufacture of injectables such as biologics (including vaccines and ATMP); and is also an ingredient in parenteral, heamofiltration solutions and haemodiafiltration solutions, peritoneal dialysis solutions, and irrigation solutions. Any container or closure involved in the manufacture of such products must therefore have a final rinse at minimum using WFI.
What is WFI?
WFI quality water has low conductivity, low total organic carbon (TOC) levels, virtually no viable organisms and low endotoxin allowances. The water is typically generated using a combination of filtration, reverse osmosis, and distillation and is stored prior to use heated at around 70-80ᵒC. The specifications of WFI are set in the US Pharmacopoeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) documents.
What is the difference between rinse and clean?
The definition of rinse is to wash an item quickly using only water while the definition of cleaning is to remove dirt. For many pharmaceutical devices manufactured in a clean environment rinsing with WFI may be the only process required to create a clean device. For other devices an initial wash stage may be required using chemicals prior to final rinse. If chemicals are used in an initial wash stage then the rinse stage must be sufficient to remove any trace of the chemicals.
Why is water pressure important?
Pressure controls are necessary when cleaning pharmaceutical containers and closures. Increased pressure creates turbulence on the material surface, aiding the removal of left-over residues from the container or closure’s fabrication process. Too much pressure may cause damage to the container or closure to be cleaned, so pressure controls must be optimised as part of the cleaning process qualification activities. Ultrasonics can be used as an alternative to water pressure.
Why is the cleaning water temperature important?
Increasing WFI temperature in a rinsing process increases the solubility and break-down rate of any residues left on a container or closure left over from its fabrication process. Increased cleaning temperatures therefore increase the efficiency and effectiveness of a cleaning process. A cleaning temperature of 70-80oC is recommended. WFI production and storage systems circulate the water within this temperature range to maintain the quality, as it is considered to be “self-sanitising” and less susceptible to microbiological contamination by the Food & Drug Administrative (2) and the World Health Organisation (3).
Verifying the effectiveness of a cleaning process
The effectiveness of a cleaning process with WFI can typically be verified by evaluating the reduction in endotoxin, sub-visible particles and TOC levels on the product being cleaned post processing. The standard “BS ISO 21882” sets recommendations on limits for glass vials on sub visible particles (where the limit for particles over 10µm is a maximum of 600; and particles over 25µm is a maximum of 60 using the light obstruction test method) and endotoxins (where the limit is less than 0.25 Endotoxin units (EU) per ml) which can be used as a basis for wider range of devices (4). For TOC levels the standard “ISO 19227” sets a limit of 0,5mg for an implant which can be used as a basis (5).
A common method of verifying the cleaning coverage on the interior surfaces of a container is to coat them with riboflavin solution (fluorescent under UV light), leave to dry, feed the product through the cleaning process and then inspect under UV light. An absence of UV light on the riboflavin spiked surfaces indicates that the WFI has rinsed the whole container.
Water for injection cleaning at Andersen Caledonia
We offer expert advice across a range of specialist services. Contact us to find out what we can do for you here.
REFERENCES
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the quality of water for pharmaceutical use. Quality of water for pharmaceutical use. 20 July 2020, pp. 1-10.
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. High Purity Water System. Inspection Guides. 2016, Vol. 7, 93.
- The World Health Organisation. Water for Pharmaceutical Use. Annex 2 – Good Manufacturing Practices. Draft Working Document for Comments, 2020, Vol. 20.842, Rev 1 .
- British Standards Institute. Sterile packaged ready for filling glass vials. Switzerland : British Standards Institute, 2019. BS ISO 21882.
- British Standards Institute. Implants for surgery — Cleanliness of orthopedic implants — General requirements. Switzerland : British Standards Institute, 2018. ISO 19227.
Share: